What is Product Data Management?
Author name: Bradley Taylor
Every product has a story to tell before it reaches a customer. An idea sparks, teams draft designs, build prototypes, and refine them into a finished item ready for the market. Along the way, they generate a mountain of technical information that must stay organized, accurate, and easy to find.
Product Data Management software helps keep that information in order. It gives engineering and manufacturing teams a clear framework for managing product data, staying on top of changes, and working together without confusion.
This guide explains what PDM is, how it works, the benefits it offers, its main components, and how it compares with PLM and PIM. The goal is to show how the right software solution for product data can strengthen business processes and improve the customer experience.
PDM Handles Engineering. PIM Drives Ecommerce Sales.
While PDM focuses on engineering data, ecommerce teams need a different solution. Learn how PIM systems manage the product content that actually drives sales.
What is Product Data Management (PDM)?
Product Data Management is a system that organizes all files and information related to product design and engineering. Instead of scattered folders and unclear ownership, everything is stored in one structured platform with permissions, workflows, and access control.
Companies of all sizes ask the same question: “What is PDM going to do for us?” The answer is straightforward. It makes product development more accurate, efficient, and secure. According to Gartner, poor data quality costs organizations an average of $12.9 million per year and creates long-term challenges by making ecosystems more complex and decisions less reliable.
PDM can help prevent these problems.
Definition and Core Functions
The definition of PDM is a tool that provides structure for product-related files and documents. The core functions of PDM include:
- Central file storage with clear ownership
- Version control to manage changes
- Workflow automation for approvals and reviews
- Integration with other systems, like ERP and PLM software
- Data security through role-based access control
Types of Data Managed by PDM
The strength of a PDM solution is its ability to manage many forms of product data. Examples include:
- CAD drawings and engineering designs
- Bills of Materials (BOMs)
- Technical specifications
- Testing results and quality assurance reports
- Compliance and certification records
- Manufacturing instructions and process sheets
- Supporting documents like manuals or assembly guides
Who Uses PDM Systems
A wide range of roles rely on the PDM system, including:
- Engineering teams creating designs and prototypes
- Manufacturing teams that need accurate instructions
- Quality managers ensuring compliance data is correct
- Project managers monitoring timelines and updates
- IT specialists integrating PDM with ERP or resource planning tools
- Data teams that keep information structured for reporting
How Product Data Management Works
A PDM platform structures the entire process of creating, reviewing, updating, and distributing product data. It ensures teams work with accurate and controlled information at every stage.
Data Creation and Collection
Every product begins with design files, CAD drawings, or specifications. At this stage, engineering software tools generate the initial set of data. Then, PDM collects and stores these files in a central database. This makes them accessible to the rest of the team without duplication.
Review and Approval Process
Once files are created, they must go through approvals. A PDM system uses built-in workflows to enable easy access for managers, quality teams, or compliance officers. These features enforce consistency and accountability.
Distribution and Updates
When approved, information is distributed across the organization. Manufacturing teams use the data to build products. Retail and ecommerce teams may receive supporting documentation. Updates are tracked automatically, and outdated versions are removed from circulation.
Version Control and Change Management
One of the most powerful features of PDM is version control. Every change is logged. Users can see who made edits, when they happened, and why. If mistakes occur, older versions can be restored. This structured approach to change management prevents costly errors and supports continuous improvement.
Benefits of Product Data Management Software
Using a PDM system changes the way teams handle product work. The right setup saves time, reduces mistakes, and makes collaboration easier across the organization.
Centralized Data Storage
When files are scattered between drives and email threads, everything becomes slower. A PDM platform keeps files centralized in one location, which means teams can access them where they know to look. This reduces duplication and prevents costly errors.
Improved Team Collaboration
Product development will typically involve many groups: design, manufacturing, marketing, and even sales. A PDM tool harmonizes them all by making sure that they are all using the same proper data. In ecommerce, this is especially important when technical specifications must feed into the systems that deliver content to customers seamlessly.
Faster Product Development
With streamlined workflows and automated approvals, teams spend less time waiting. Products move from concept to launch faster. For businesses in competitive retail industries, speed to market can be a deciding factor in success.
Enhanced Data Security
A strong PDM system reduces security risks by limiting exposure of sensitive product data. Intellectual property remains protected, and regulatory requirements are easier to meet when data is consistently monitored and controlled. Teams gain confidence that confidential information stays in the right hands.
See How PIM Delivers These Same Benefits for Ecommerce
Centralized data, better collaboration, faster launches—PIM brings all these advantages to your product content. Discover the top 8 benefits of using PIM for ecommerce success.
Major Components of PDM Systems
Every effective PDM solution includes several important components. These features work together to create an environment where product data is accurate and secure.
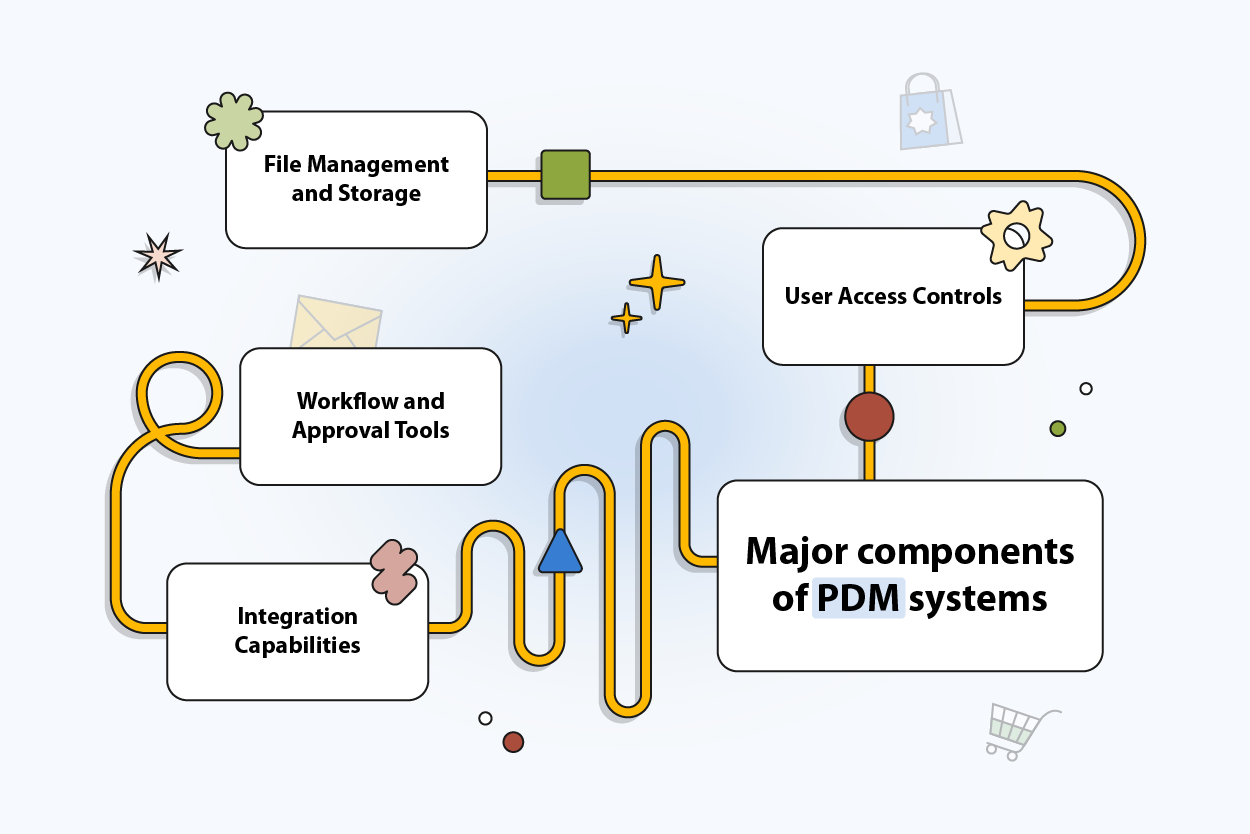
File Management and Storage
File management ensures every CAD drawing, BOM, and instruction sheet has a home. Files are indexed, tagged, and easily searchable.
Workflow and Approval Tools
Workflows give structure to the approval process. A system can automatically notify managers when files need review, track their decisions, and log the results.
Integration Capabilities
A strong PDM platform integrates with ERP, PLM, and other business software. These connections extend the reach of PDM into areas like resource planning, procurement, and compliance.
User Access Controls
Access controls define exactly who can view, edit, or approve files within the PDM platform. Permissions are role-based, giving administrators fine-grained oversight. This feature keeps collaboration efficient while ensuring only authorized users interact with critical information.
What is the Difference Between PDM and PLM?
PDM and PLM software often overlap, but they serve different needs.
PDM Focus: Design and Development Phase
PDM centers on organizing product data during design and engineering. Its primary role is controlling files, managing version control, and supporting collaboration within technical teams.
PLM Focus: Complete Product Lifecycle
PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) goes further. It manages the full lifecycle, from idea to disposal. PLM covers business processes across manufacturing, marketing, retail, service, and recycling.
Research from CIMdata indicates that over 90% of industrial companies generating more than $100 million in revenue rely on PLM to drive digital transformation, standardize operations, and accelerate time-to-market.
When to Use Each System
Choosing between PDM and PLM depends on the type of work your teams do and the level of visibility you need.
A PDM system is the right fit when the main pain point is controlling engineering files. PDM keeps the design process organized and secure. It’s especially valuable for companies focused on product development but not yet ready for broader lifecycle oversight.
A PLM system, on the other hand, becomes important when product complexity and scale increase. PLM connects the dots across every stage of the lifecycle. Organizations with global supply chains, strict compliance requirements, or fast-moving portfolios often need that wider scope.
Ready to Choose Your Product Data Solution?
Choosing between PDM, PLM, and PIM can be complex. Our comprehensive guide walks you through 15 critical criteria to help you select the right system for your business needs.
What is the Difference Between PDM and PIM?
In ecommerce, a common question is how PDM compares to PIM (Product Information Management).
PDM: Engineering and Technical Data
PDM handles technical, engineering-focused product information. It is the home of CAD files, BOMs, and compliance records.
PIM: Marketing and Sales Data
A Product Information Management (PIM) system is designed for the data that drives sales and shapes the buying experience. Unlike PDM, PIM focuses on product content used by marketing and retail teams.
This includes:
- Product names and detailed descriptions
- Images, videos, and other digital assets
- Pricing and promotional details
- Variants such as sizes, colors, and configurations
- Translations and localized content for global markets
- Channel-specific attributes required by marketplaces and advertising platforms
Why E-commerce Needs PIM, Not PDM
Ecommerce teams work in a very different environment from engineering or manufacturing groups. They aren’t focused on CAD drawings or bills of material. Their role is to deliver products to market, which means handling large volumes of customer-facing information quickly and accurately.
A PIM solution organizes product titles, descriptions, images, attributes, and pricing in one structured system. It provides workflows to enrich content, adapt it for multiple markets, and publish to every retail and ecommerce channel.
Without a dedicated PIM, teams often rely on spreadsheets or ERP systems, which are not designed for high-volume content. The outcome is inconsistent attributes, errors across channels, and lost sales opportunities.
A PIM system removes that risk by making product content the single source of truth for marketing and sales. It improves time to market, strengthens the customer experience, and gives customers confidence that the products they see online are complete and reliable.
PDM manages technical files, but online stores run on customer-facing product content. To keep product data accurate and consistent for every channel, ecommerce teams need PIM.
Choosing the Right Product Data Management Solution
When considering a PDM system, leaders should recognize its role in the broader technology stack. PDM delivers value for engineering-driven companies where managing technical information and enforcing version control are essential. Teams in manufacturing need these features to reduce errors and keep development on schedule.
For ecommerce businesses, the decision is different. PDM may still have a place if products are designed in-house and engineering files must be tightly controlled. But for organizations that rely on supplier data and focus on selling, PDM alone will not meet daily needs. The better investment is a PIM platform that can connect product attributes, marketing content, and channel feeds in one system.
A practical approach is to assess the type of data your team works with most. If it is engineering drawings and technical documentation, prioritize PDM. If it is descriptions, media, and sales attributes, prioritize PIM. Many companies use both, but ecommerce teams almost always benefit more from PIM.
PIMinto provides solutions designed for this reality. Our software gives ecommerce teams the control and flexibility to manage large catalogs, improve collaboration, and deliver accurate content to every channel.Ecommerce Teams Need PIM, Not PDM
If your priority is winning customers with consistent, high-quality product data, a dedicated PIM system like PIMinto is the smarter choice. Book a demo today to see how PIMinto helps your team deliver sales-ready product data to every channel.
Modified on: 2025-09-09